Amazon was officially established on July 5, 1994, by Jeff Bezos. The company started as an online bookstore operating out of Bezos’s garage in Bellevue, Washington. Jeff Bezos initially chose the name “Cadabra,” short for “abracadabra,” but later changed it to “Amazon” because he wanted a name that began with the letter ‘A’ to increase its chances of being listed at the top of alphabetical lists.

Today, Amazon is not only an e-commerce giant but also a major player in cloud computing, artificial intelligence, digital entertainment, and more. The company’s journey from a humble online bookstore in a garage to a global tech behemoth is a remarkable example of entrepreneurial success and innovation.
History and Timeline of Amazon:
Over the years, Amazon rapidly diversified its offerings, expanding into various product categories. In 2000, it introduced the Marketplace platform, allowing third-party sellers to offer their products. Amazon Prime, a subscription service offering benefits like free two-day shipping, was introduced in 2005.
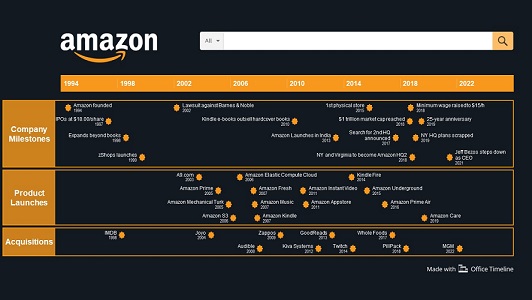
The company continued its expansion with ventures like Amazon Web Services (AWS) in 2006, Kindle e-readers in 2007, and the acquisition of Whole Foods Market in 2017. Amazon’s growth has been marked by innovation, strategic acquisitions, and a focus on customer experience, making it a global e-commerce and technology giant by continually adapting to market demands.
The company continued its expansion with ventures like Amazon Web Services (AWS) in 2006, Kindle e-readers in 2007, and the acquisition of Whole Foods Market in 2017. Amazon’s growth has been marked by innovation, strategic acquisitions, and a focus on customer experience, making it a global e-commerce and technology giant by continually adapting to market demands.
Amazon Web Services:
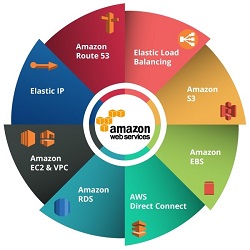
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a comprehensive cloud computing platform provided by Amazon.com. Launched in 2006, AWS offers a wide array of computing resources, storage solutions, and scalable services that enable businesses, developers, and organizations to build and deploy applications more efficiently and cost-effectively. AWS provides a flexible and on-demand infrastructure, allowing users to access computing power, storage, and other functionalities without the need for extensive upfront investments.
Services within AWS include computing power with Amazon EC2, storage with Amazon S3, and a variety of tools for machine learning, analytics, and database management. It has become a dominant force in the cloud computing industry, serving millions of customers worldwide and powering numerous websites, applications, and enterprises across diverse sectors.
Amazon Region:
Amazon has separate websites or regions catering to different countries and amazon regions around the world. Here are some of the major Amazon websites for different regions:
- Amazon.com: This is the main Amazon website, primarily serving customers in the United States. However, it also ships to many other countries.
- Amazon.co.uk: Serving customers in the United Kingdom and Ireland.
- Amazon.ca: Catering to customers in Canada.
- Amazon.de: Serving customers in Germany, Austria, and Luxembourg.
- Amazon.fr: Serving customers in France and Monaco.
- Amazon.it: Serving customers in Italy, San Marino, and Vatican City.
- Amazon.es: Catering to customers in Spain.
- Amazon.co.jp: Serving customers in Japan.
- Amazon.in: Focused on customers in India.
- Amazon.com.br: Catering to customers in Brazil.
- Amazon.com.mx: Serving customers in Mexico.
- Amazon.com.au: Focused on customers in Australia.
- Amazon.nl: Serving customers in the Netherlands.
- Amazon.sg: Catering to customers in Singapore.
- Amazon.cn: Focused on customers in China.


Introduction to Amazon
misreferred xyandanxvurulmus.9Y9cyPCGhXoa